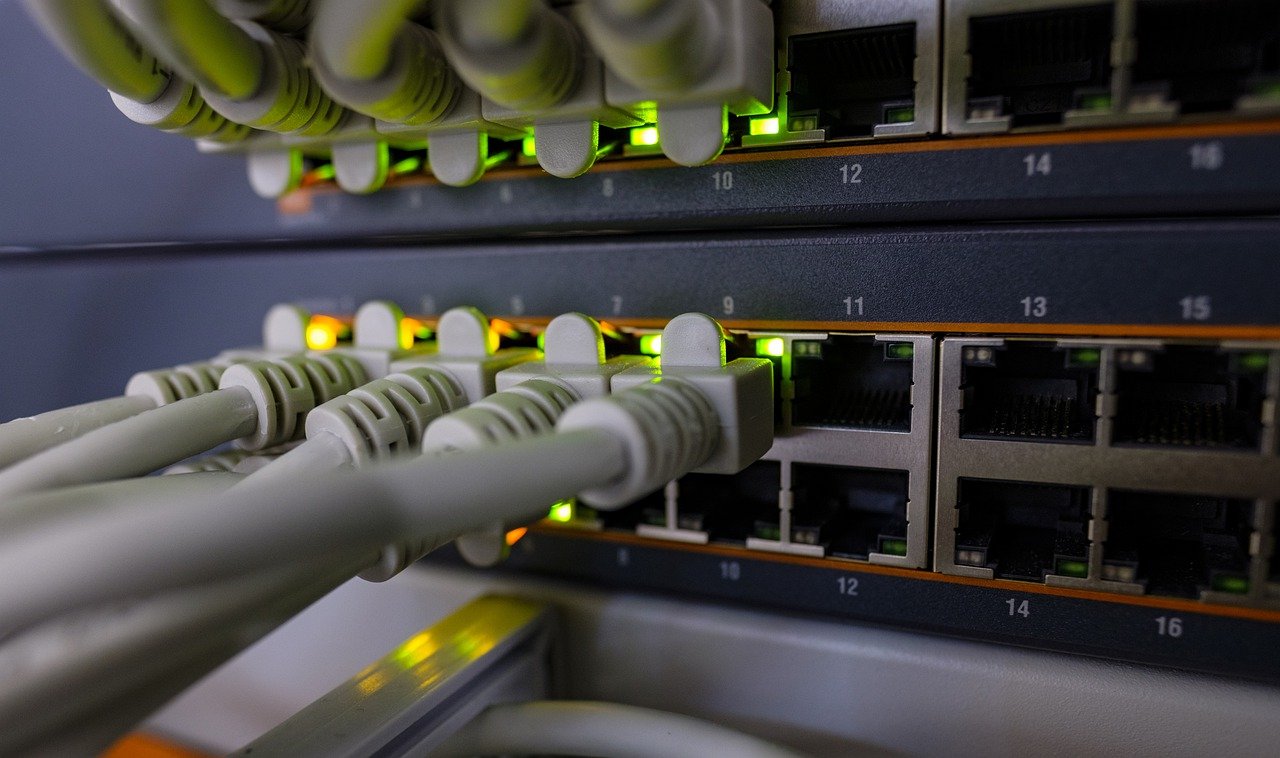
As businesses and households increasingly rely on high-speed internet connectivity, it’s essential to understand the various broadband technologies available in the UK. In this post, we’ll explore the differences between FTTC, FTTP, and leased lines, their respective advantages, and their suitability for different use cases.
Fibre-to-the-Cabinet (FTTC)
FTTC is a widely adopted broadband technology in the UK, which involves running fibre optic cables from the exchange to the street cabinet. From the cabinet, copper lines are used to connect to individual premises. This hybrid approach allows for faster download speeds compared to traditional ADSL broadband, typically ranging from 30 Mbps to 80 Mbps. However, upload speeds are generally lower, making FTTC less suitable for applications that require substantial upstream bandwidth.
Fibre-to-the-Premises (FTTP)
FTTP, also known as full-fibre broadband, is the most advanced and future-proof broadband technology. As the name suggests, fibre optic cables are run directly to the premises, eliminating the need for copper lines. With FTTP, both download and upload speeds are significantly higher, often reaching gigabit speeds (1 Gbps or more). This symmetric bandwidth makes FTTP ideal for businesses, remote workers, and households with high data demands, such as video conferencing, cloud computing, and online gaming.
Leased Lines
Leased lines, also known as private circuits, are dedicated point-to-point connections that provide businesses with a private, uncontended, and highly secure internet connection. Unlike broadband technologies that share bandwidth among multiple users, leased lines offer dedicated bandwidth for the exclusive use of a single organization. Leased lines are typically more expensive than other broadband options but offer unmatched reliability, low latency, and higher upload and download speeds, making them suitable for mission-critical applications, such as data centres, financial institutions, and organizations with large data transfer requirements.
In summary, FTTC and FTTP are broadband technologies designed for residential and small business use, with FTTP offering superior performance and future-proofing. Leased lines are dedicated internet access services tailored for larger businesses and organizations with higher bandwidth demands and stringent reliability requirements. The choice between these technologies depends on factors such as bandwidth needs, budget, and the specific use case.